Task Queues
Task queues hold time-ordered sets of information that require processing, either by individuals or computer algorithms. Tasks can be scheduled, prioritized, and assigned to owners. Larger tasks might include subtasks or milestones. However, the task queue itself does not specify the type of data it contains; any type of data can be pushed onto a queue. It is the responsibility of the application developer to define the data types and ensure the consistency of the queue’s contents.
The service uses RabbitMQ for task management. The latter is not exposed to developers; however, it is managed by an abstract set of API wrappers that ensure easy, fault-tolerant, access to the underlying message queuing framework.
To start using the service, login to the ADSP Tenant-management-webapp and select the Task Service. There you will be able to create your first task queue. Queues are identified by a namespace:name pair which you specify when creating one. There is no particular significance to the naming convention, it just gives you a means to help organize things when the number of queues in your tenant are large.
Metrics
Several queue metrics are tracked by the Task Service, including
- the average, min, and max size of the queue
- the number of tasks created, completed, and cancelled since queue creation
- the number of tasks with a given status
- the number of tasks with a given priority
- the average, minimum, and maximum number of active tasks
The metrics can be filtered by active tasks only, and the information restricted to just status and priority metrics.
Security
Developers must assign access roles to each queue created. The Task Service defines two types of users:
- Assigner: Assigners are able to assign tasks to individuals for completion.
- Worker: Workers are those that can complete a task.
In the Tenant-Management-Webapp developers can assign user types to one or more tenant-defined keycloak roles. Note: this security is important enough that this step is mandatory. If, when testing you find you are getting 403’s, make sure your test user has the right tenant-defined roles. You can assign user types to these roles via the Queue permissions pane in the Queue editor:
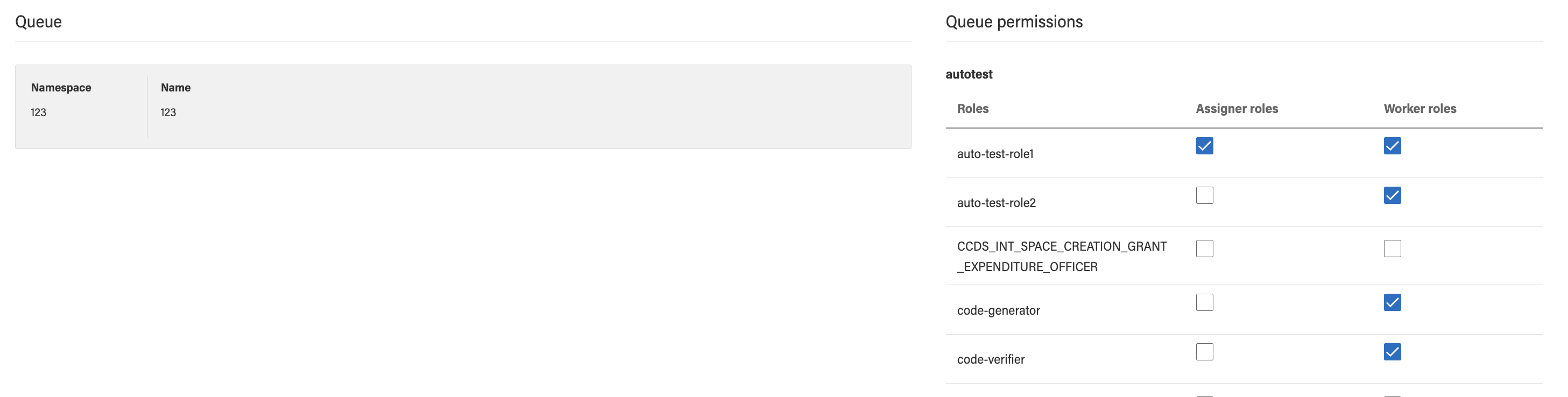
In addition to the queue specific roles, users must have one or more of the following in order to access any task related data:
- task-reader: Users can see the task data, but are unable to update it.
- task-writer: Users can update task data
- task-admin: Users can assign tasks to other individuals.
APIs
Once your queue is created you can then start accessing it through the APIs. There are endpoints to:
- push data onto a queue
- assign individuals to a task
- retrieve lists of workers and assigners
- retrieve queue metrics
as well as other, basic, CRUD operations. Note: you cannot remove queues that have tasks within them.
Events
Various events are triggered throughout the lifecycle of a task. These events can notify users about important developments. Additionally, all events are logged to ensure traceability and auditability. The events include:
- task-updated
- task-created
- task-priority-set
- task-assigned
- task-started
- task-completed
- task-cancelled